Polylactic Acid (PLA) filament has become a popular choice among 3D printing enthusiasts and professionals alike. But what is the real story behind PLA filament and toxicity? This article aims to delve into the origins of PLA, its properties, and the safety concerns surrounding its use.
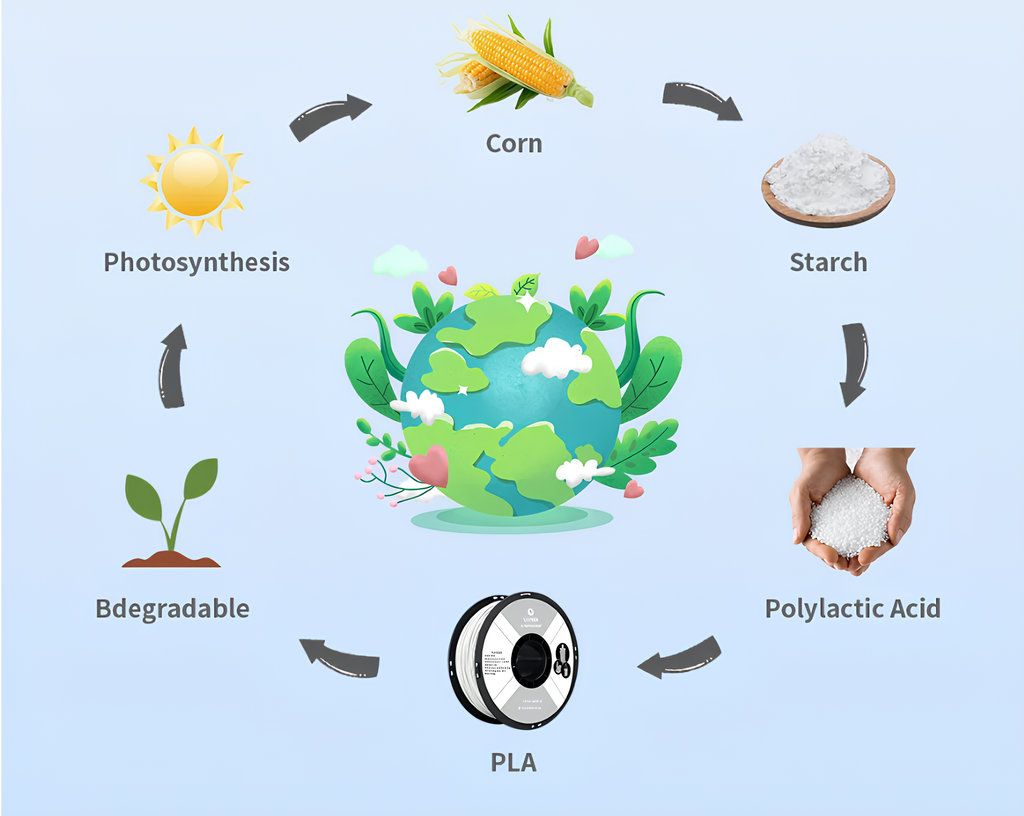
The Origins of PLA Filament
PLA is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane. This biopolymer is produced through the fermentation of sugars, which are then polymerized to create long chains of lactic acid. The result is a material that is not only eco-friendly but also easy to print with, making it a favorite in the 3D printing community.
Properties of PLA
One of the key advantages of PLA filament is its low melting temperature, typically around 180-220°C. This allows for easier printing and reduces the risk of warping. Additionally, PLA is known for its excellent layer adhesion and vibrant colors, which can enhance the aesthetic appeal of printed objects. However, while PLA is praised for its user-friendly properties, questions about its safety and toxicity have emerged.
The Real Story Behind PLA Filament and Toxicity
When discussing the real story behind PLA filament and toxicity, it is essential to consider the materials used in its production. PLA is generally regarded as safe for food contact, as it is made from natural sources. However, some concerns arise when PLA is heated during the printing process. The potential release of harmful substances, such as lactide and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs), has led to debates about its safety.
- PLA is considered non-toxic and safe for most applications.
- Heating PLA can produce fumes that may be irritating to some individuals.
- Proper ventilation is recommended during the printing process.
For those interested in a deeper understanding of PLA's safety, you can explore more about its toxicity concerns in this detailed article.
Comparing PLA with Other Filaments
When evaluating the safety of PLA, it is also beneficial to compare it with other common 3D printing materials. For instance, ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is known to emit more harmful fumes when heated, making PLA a safer alternative for home users. Additionally, PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) is another popular filament that is considered safe but may not be as biodegradable as PLA.
Conclusion: Making Informed Choices
In conclusion, the real story behind pla filament and toxicity is multifaceted. While PLA is generally safe and eco-friendly, it is crucial to be aware of the potential risks associated with its use, particularly during the printing process. By ensuring proper ventilation and understanding the properties of PLA, users can enjoy the benefits of this versatile material while minimizing any health concerns.
As the 3D printing industry continues to evolve, ongoing research will further clarify the safety of various materials, including PLA. Staying informed and making educated choices will empower users to harness the full potential of 3D printing technology.