Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is one of the most popular methods of 3D printing, widely recognized for its accessibility and versatility. This technology has transformed how we approach manufacturing, prototyping, and even personal projects. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the FDM 3D printer, exploring its mechanisms, applications, and advantages.
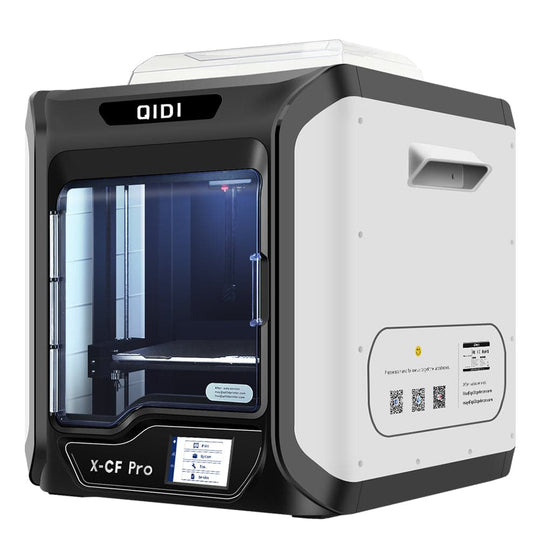

What is an FDM 3D Printer?
An FDM 3D printer operates by extruding thermoplastic filament through a heated nozzle, which melts the material and deposits it layer by layer to create a three-dimensional object. This process is often referred to as additive manufacturing, as it builds objects by adding material rather than subtracting it. But how does this technology work in practice?
- Filament Selection: The choice of filament is crucial. Common materials include PLA, ABS, and PETG, each offering different properties.
- Heating Mechanism: The nozzle heats up to a specific temperature to melt the filament, allowing it to flow smoothly.
- Layering Process: The printer moves in the X, Y, and Z axes, depositing material layer by layer until the object is complete.
Applications of FDM 3D Printing
The versatility of the FDM 3D printer allows it to be utilized across various industries. Here are some notable applications:
- Prototyping: Rapid prototyping is one of the most significant advantages of FDM technology, enabling designers to create functional prototypes quickly.
- Education: Many educational institutions use FDM printers to teach students about engineering and design principles.
- Healthcare: Custom medical devices and anatomical models can be produced, enhancing patient care and surgical planning.
- Manufacturing: Small-scale production runs can be efficiently executed, reducing lead times and costs.
Advantages of Using an FDM 3D Printer
Why should you consider using an FDM 3D printer? Here are some compelling reasons:
- Cost-Effective: FDM printers are generally more affordable than other 3D printing technologies, making them accessible to hobbyists and small businesses.
- Ease of Use: Many FDM printers come with user-friendly interfaces and software, simplifying the printing process.
- Material Variety: A wide range of filaments is available, allowing users to select materials based on their specific needs.
Conclusion
In summary, the FDM 3D printer represents a significant advancement in manufacturing and design technology. Its ability to produce high-quality, customized objects quickly and affordably makes it an invaluable tool across various sectors. Whether you are a professional engineer, a student, or a hobbyist, understanding the fundamentals of FDM printing can open up new possibilities for creativity and innovation.
For those interested in exploring high-quality FDM 3D printers, consider visiting  for a selection of advanced models that can meet your printing needs.
for a selection of advanced models that can meet your printing needs.